UK Releases Code of Practice for Consumer IoT Security
Steve Lipner, Executive Director
This week, the UK Government’s Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport (DCMS) released a Code of Practice for the secure design of internet-connected consumer devices and their associated services. The voluntary Code of Practice is composed of 13 secure development and design guidelines for IoT manufactures and other stakeholders. DCMS developed the document in conjunction with the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC). It also engaged with numerous industry associations, and SAFECode was pleased to contribute its secure development guidance to the process.
The guidelines in the Code of Practice are primarily outcome-based and seek to allow organizations the flexibility to continue to innovate and develop security solutions for their products. However, DCMS also offers a complementary reference guide that maps the Code of Practice against published standards, recommendations and guidance on IoT security and privacy from around the world. In fact, the mapping references around 100 documents from nearly 50 organizations. While not exhaustive, it offers a large collection of guidance available to date on IoT security and should be a valuable reference for any organization seeking to learn more about IoT-specific security practices.
Notably, the Code of Practice and its mapping document emphasize that these 13 guidelines are not a silver bullet for IoT security. Rather, it states that organizations that seek to create secure IoT must shift to a security mindset and invest in a secure development lifecycle process. Products and services should be designed with security in mind, from product development through their entire lifecycle. This process-based approach is fundamental to the successful execution of the Code of Practice, and DCMS points to SAFECode’s Fundamental Practices for Secure Software Development as a key reference for those seeking to implement or improve a secure development process. SAFECode also recommends that organizations take advantage of our free training modules to further support their efforts.
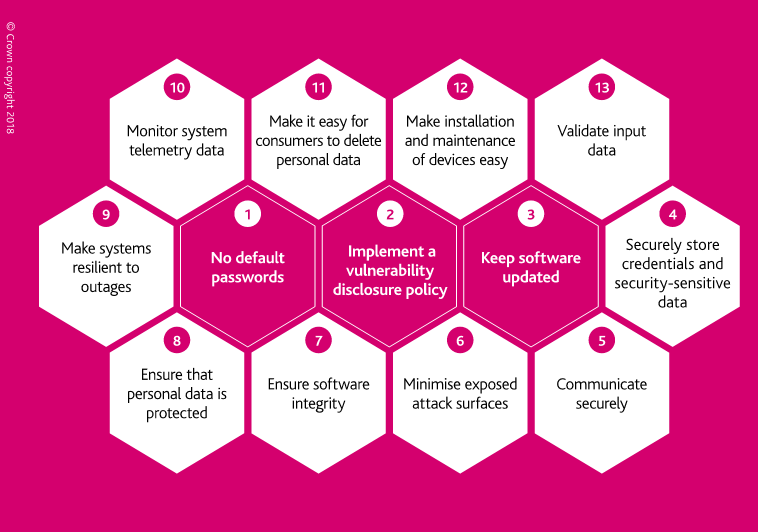
Code of Practice for Consumer IoT Security
*Excerpt from DCMS Code of Practice for Consumer IoT Security
- No default passwords
- Implement a vulnerability disclosure policy
- Keep software updated
- Securely store credentials and security-sensitive data
- Communicate securely
- Minimize exposed attack surfaces
- Ensure software integrity
- Ensure that personal data is protected
- Make systems resilient to outages
- Monitor system telemetry data
- Make it easy for consumers to delete personal data
- Make installation and maintenance of devices easy
- Validate input data
For more information and additional supporting documentation, visit: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/secure-by-design. DCMS will periodically review the Code and publish updates, at least every two years. If you’d like to stay up-to-date on new developments, DCMS asks that you contact [email protected].